TDD
Test Driven Development
What is Test Driven Development (TDD)?
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software development approach in which test cases are developed to specify and validate what the code will do. In simple terms, test cases for each functionality are created and tested first and if the test fails then the new code is written in order to pass the test and make the code simple and bug-free.
Test-Driven Development starts with designing and developing tests for every small functionality of an application. TDD framework instructs developers to write new code only if an automated test has failed. This avoids duplication of code. The TDD full form is Test-driven development.

The simple concept of TDD is to write and correct the failed tests before writing new code (before development). This helps to avoid duplication of code as we write a small amount of code at a time in order to pass tests. (Tests are nothing but requirement conditions that we need to test to fulfill them).
Test-Driven development is a process of developing and running automated tests before the actual development of the application. Hence, TDD is sometimes also called Test First Development.
How to perform TDD Test
The following steps define how to perform the TDD test,
Add a test.
Run all tests and see if any new test fails.
Write some code.
Run tests and Refactor code.
Repeat.

Some clarifications about TDD:
TDD approach is neither about “Testing” nor about “Design”.
TDD does not mean “write some of the tests, then build a system that passes the tests.
TDD does not mean “do lots of Testing.”
TDD Vs. Traditional Testing
Below is the main difference between Test driven development and traditional testing:
TDD approach is primarily a specification technique. It ensures that your source code is thoroughly tested at a confirmatory level.
With traditional testing, a successful test finds one or more defects. It is the same as TDD. When a test fails, you have made progress because you know that you need to resolve the problem.
TDD ensures that your system actually meets the requirements defined for it. It helps to build your confidence in your system.
In TDD more focus is on production code that verifies whether testing will work properly. In traditional testing, more focus is on test case design. Whether the test will show the proper/improper execution of the application in order to fulfill requirements.
In TDD, you achieve 100% coverage test. Every single line of code is tested, unlike traditional testing.
The combination of both traditional testing and TDD leads to the importance of testing the system rather than the perfection of the system.
In Agile Modeling (AM), you should “test with a purpose”. You should know why you are testing something and what level its needs to be tested.
What are acceptance TDD and Developer TDD?
There are two levels of TDD
Acceptance TDD (ATDD): With ATDD you write a single acceptance test. This test fulfills the requirement of the specification or satisfies the behavior of the system. After that write just enough production/functionality code to fulfill that acceptance test. Acceptance test focuses on the overall behavior of the system. ATDD also was known as Behavioral Driven Development (BDD).
Developer TDD: With Developer TDD you write a single developer test i.e. unit test and then just enough production code to fulfill that test. The unit test focuses on every small functionality of the system. Developer TDD is simply called TDD. The main goal of ATDD and TDD is to specify detailed, executable requirements for your solution on a just-in-time (JIT) basis. JIT means taking only those requirements into consideration that are needed in the system. To increase efficiency.

Scaling TDD via Agile Model Driven Development (AMDD)
TDD is very good at detailed specification and validation. It fails at thinking through bigger issues such as overall design, use of the system, or UI. AMDD addresses the Agile scaling issues that TDD does not.
Thus AMDD is used for bigger issues.
The lifecycle of AMDD
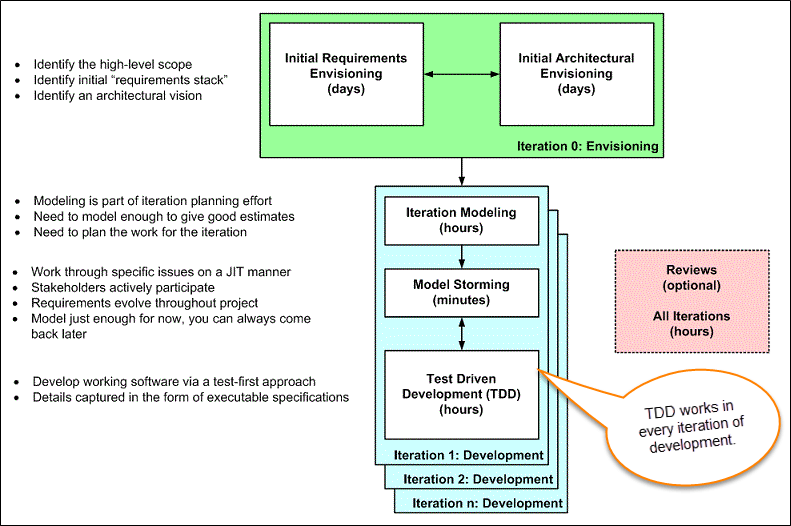
In Model-driven Development (MDD), extensive models are created before the source code is written. Which in turn has an agile approach?
In the above figure, each box represents a development activity.
Envisioning is one of the TDD processes of predicting/imagining tests which will be performed during the first week of the project. The main goal of envisioning is to identify the scope of the system and the architecture of the system. High-level requirements and architecture modeling is done for successful envisioning.
It is the process where not a detailed specification of software/system is done but exploring the requirements of software/system which defines the overall strategy of the project.
Iteration 0: Envisioning
There are two main sub-activates.
Initial requirements envisioning. It may take several days to identify high-level requirements and the scope of the system. The main focus is to explore the usage model, Initial domain model, and user interface model (UI).
Initial Architectural envisioning. It also takes several days to identify the architecture of the system. It allows for setting technical directions for the project. The main focus is to explore technology diagrams, User Interface (UI) flow, domain models, and Change cases.
Iteration modeling
The team must plan the work that will be done for each iteration.
An agile process is used for each iteration, i.e. during each iteration, a new work item will be added with priority.
First higher prioritized work will be taken into consideration. Work items added may be reprioritized or removed from the items stack at any time.
The team discusses how they are going to implement each requirement. Modeling is used for this purpose.
Modeling analysis and design are done for each requirement that is going to implement for that iteration.
Model storming
This is also known as Just in time Modeling.
Here modeling session involves a team of 2/3 members who discuss issues on paper or whiteboard.
One team member will ask another to model with them. This modeling session will take approximately 5 to 10 minutes. Where team members gather together to share whiteboard/paper.
They explore issues until they don’t find the main cause of the problem. Just in time, if one team member identifies the issue which he/she wants to resolve then he/she will take quick help of other team members.
Other group members then explore the issue and then everyone continues on as before. It is also called as stand-up modeling or customer QA sessions.
Test Driven Development (TDD)
It promotes confirmatory testing of your application code and detailed specification.
Both acceptance tests (detailed requirements) and developer tests (unit test) are inputs for TDD.
TDD makes the code simpler and clear. It allows the developer to maintain less documentation.
Reviews
This is optional. It includes code inspections and model reviews.
This can be done for each iteration or for the whole project.
This is a good option to give feedback on the project.
Test Driven Development (TDD) Vs. Agile Model Driven Development (AMDD)
TDD shortens the programming feedback loop
AMDD shortens modeling feedback loop.
TDD is detailed specification
AMDD works for bigger issues
TDD promotes the development of high-quality code
AMDD promotes high-quality communication with stakeholders and developers.
TDD speaks to programmers
AMDD talks to Business Analyst, stakeholders, and data professionals.
TDD non-visually oriented
AMDD visually oriented
TDD has limited scope to software works
AMDD has a broad scope including stakeholders. It involves working towards a common understanding
Both support evolutionary development
——————————————–
TDD Frameworks
Here is the list of best test-driven development (TDD) frameworks
Junit
TestNG
csUnit and NUnit
Rspec
Now, let’s learn Test Driven Development by example.
Example of TDD
Here in this Test Driven Development example, we will define a class password. For this class, we will try to satisfy following conditions.
A condition for Password acceptance:
The password should be between 5 to 10 characters.
First, in this TDD example, we write the code that fulfills all the above requirements.

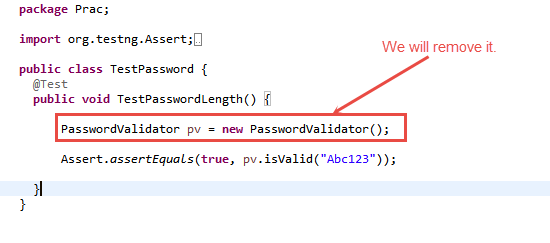
Scenario 1: To run the test, we create the class PasswordValidator ();

We will run the above class TestPassword ();
Output is PASSED as shown below;
Output:

Scenario 2: Here we can see in the method TestPasswordLength () there is no need of creating an instance of class PasswordValidator. Instance means creating an object of class to refer the members (variables/methods) of that class.
We will remove class PasswordValidator pv = new PasswordValidator () from the code. We can call the isValid () method directly by PasswordValidator. IsValid (“Abc123”). (See image below)
So we Refactor (change code) as below:
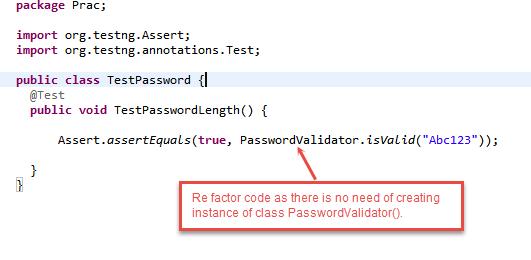
Scenario 3: After refactoring the output shows failed status (see image below) this is because we have removed the instance. So there is no reference to non –static method isValid ().

So we need to change this method by adding “static” word before Boolean as public static boolean isValid (String password). Refactoring Class PasswordValidator () to remove above error to pass the test.

Output:
After making changes to class PassValidator () if we run the test then the output will be PASSED as shown below.

Advantages of TDD
The following are the main advantages of Test Driven Development in Software Engineering:
Early bug notification.
Developers test their code but in the database world, this often consists of manual tests or one-off scripts. Using TDD you build up, over time, a suite of automated tests that you and any other developer can rerun at will.
Better Designed, cleaner and more extensible code.
It helps to understand how the code will be used and how it interacts with other modules.
It results in better design decisions and more maintainable code.
TDD allows writing smaller code having single responsibility rather than monolithic procedures with multiple responsibilities. This makes the code simpler to understand.
TDD also forces to write only production code to pass tests based on user requirements.
Confidence to Refactor
If you refactor code, there can be possibilities of breaks in the code. So having a set of automated tests you can fix those breaks before release. Proper warning will be given if breaks found when automated tests are used.
Using TDD, should results in faster, more extensible code with fewer bugs that can be updated with minimal risks.
Good for teamwork
In the absence of any team member, other team members can easily pick up and work on the code. It also aids knowledge sharing, thereby making the team more effective overall.
Good for Developers
Though developers have to spend more time in writing TDD test cases, it takes a lot less time for debugging and developing new features. You will write cleaner, less complicated code.
Summary
TDD stands for Test-driven development.
TDD meaning: It is a process of modifying the code in order to pass a test designed previously.
It more emphasis on production code rather than test case design.
Test-driven development is a process of modifying the code in order to pass a test designed previously.
In Software Engineering, It is sometimes known as “Test First Development.”
TDD testing includes refactoring a code i.e. changing/adding some amount of code to the existing code without affecting the behavior of the code.
TDD programming when used, the code becomes clearer and simple to understand.
Last updated