Singleton
Ensure a class only has one instance, and provide a global point of access to it.

Introduce
Singleton is one of 5 design patterns belonging to the Creational Design Pattern group - a group that supports class creation. It ensures that a class has only one instantiated instance and it provides access to that instance from anywhere (global access).
Use Singleton when we want:
Make sure there is only one instance of the class.
Access management is better because there is only one instance.
The number of instances of a class can be managed within specified limits.
Problem
The Singleton pattern solves two problems at the same time, violating the Single Responsibility Principle:
Ensure that a class has just a single instance. Why would anyone want to control how many instances a class has? The most common reason for this is to control access to some shared resource—for example, a database or a file.
Here’s how it works: imagine that you created an object, but after a while decided to create a new one. Instead of receiving a fresh object, you’ll get the one you already created.
Note that this behavior is impossible to implement with a regular constructor since a constructor call must always return a new object by design.
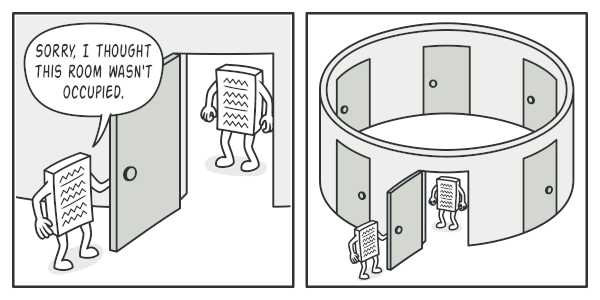
Provide a global access point to that instance. Remember those global variables that you (all right, me) used to store some essential objects? While they’re very handy, they’re also very unsafe since any code can potentially overwrite the contents of those variables and crash the app.
Just like a global variable, the Singleton pattern lets you access some object from anywhere in the program. However, it also protects that instance from being overwritten by other code.
There’s another side to this problem: you don’t want the code that solves problem #1 to be scattered all over your program. It’s much better to have it within one class, especially if the rest of your code already depends on it.
Sometimes, in the process of analyzing and designing a system, we want objects that need to exist uniquely and can be accessed anytime, anywhere. So how to realize such an object when building source code? We can think of using a global variable: public static final. However, using global variables it breaks the encapsulation rules of Object Oriented Programming.

Nowadays, the Singleton pattern has become so popular that people may call something a singleton even if it solves just one of the listed problems.
Solution
All implementations of the Singleton have these two steps in common:
Make the default constructor private, to prevent other objects from using the
newoperator with the Singleton class.Create a static creation method that acts as a constructor. Under the hood, this method calls the private constructor to create an object and saves it in a static field. All following calls to this method return the cached object.
If your code has access to the Singleton class, then it’s able to call the Singleton’s static method. So whenever that method is called, the same object is always returned.
Real-World Analogy
The government is an excellent example of the Singleton pattern. A country can have only one official government. Regardless of the personal identities of the individuals who form governments, the title, “The Government of X”, is a global point of access that identifies the group of people in charge.
Structure

Using
Make the constructor private so that the client cannot instantiate the class object
Create a private static variable that is an instance of that class to ensure that it is unique and only created in that class
Create a public static method that returns the instance just initialized above. This is the only way for other classes to access the instance of this class.
Applicability
Use the Singleton pattern when a class in your program should have just a single instance available to all clients; for example, a single database object shared by different parts of the program.
The Singleton pattern disables all other means of creating objects of a class except for the special creation method. This method either creates a new object or returns an existing one if it has already been created.
Use the Singleton pattern when you need stricter control over global variables.
Unlike global variables, the Singleton pattern guarantees that there’s just one instance of a class. Nothing, except for the Singleton class itself, can replace the cached instance.
Note that you can always adjust this limitation and allow creating any number of Singleton instances. The only piece of code that needs changing is the body of the getInstance method.
How to Implement
Add a private static field to the class for storing the singleton instance.
Declare a public static creation method for getting the singleton instance.
Implement “lazy initialization” inside the static method. It should create a new object on its first call and put it into the static field. The method should always return that instance on all subsequent calls.
Make the constructor of the class private. The static method of the class will still be able to call the constructor, but not the other objects.
Go over the client code and replace all direct calls to the singleton’s constructor with calls to its static creation method.
Pros and Cons
Pros
You can be sure that a class has only a single instance.
You gain a global access point to that instance.
The singleton object is initialized only when it’s requested for the first time.
Cons
Violates the Single Responsibility Principle. The pattern solves two problems at the time.
The Singleton pattern can mask bad design, for instance, when the components of the program know too much about each other.
The pattern requires special treatment in a multithreaded environment so that multiple threads won’t create a singleton object several times.
It may be difficult to unit test the client code of the Singleton because many test frameworks rely on inheritance when producing mock objects. Since the constructor of the singleton class is private and overriding static methods is impossible in most languages, you will need to think of a creative way to mock the singleton. Or just don’t write the tests. Or don’t use the Singleton pattern.
When to use
It can be certain that a class has only one instance
Ability to access instances from anywhere (global access)
The singleton object is only initialized once when it is first requested
Because a class using Singleton only has 1 Instance, it is often used in cases of solving problems that need to access applications such as: Shared resources, Logger, Configuration, Caching, Thread pool, ...
Some other design patterns also use Singleton to implement: Abstract Factory, Builder, Prototype, Facade,...
Relations with Other Patterns
A Facade class can often be transformed into a Singleton since a single facade object is sufficient in most cases.
Flyweight would resemble Singleton if you somehow managed to reduce all shared states of the objects to just one flyweight object. But there are two fundamental differences between these patterns:
There should be only one Singleton instance, whereas a Flyweight class can have multiple instances with different intrinsic states.
The Singleton object can be mutable. Flyweight objects are immutable.
Abstract Factories, Builders, and Prototypes can all be implemented as Singletons.
Last updated