Kanban
1. Definition of Kanban
1.1. What is Kanban?
Kanban is a term originating from Japan, first used at Toyota car company. In Japanese, Kanban is composed of the words "kan" meaning "sight" and "ban" meaning "card", so this term can be simply understood as an "information board".
The Kanban model is used as a tool to visualize tasks to be done, so project members can see where they are in the workflow. A simple way is to use whiteboards and stick colored sheets of paper underneath to describe and manage the work process.
1.2. History of the birth of Kanban
In the late 40s of the last century, Toyota Corporation was in a period of crisis due to great competition from domestic and foreign corporations. To solve that crisis, engineer Taiichi Ohno proposed a plan to improve and optimize the group's production system. This method, originally called Just-in-time , was used with the goal of keeping up with production schedules according to customer needs, based on identifying material shortages in the process.
The team used colorful Kanban cards to record information, and had them move one by one through work stations in the production line: a card could serve as an order ticket while at the work station. work, then when going to the next stop it becomes a transportation ticket.
In doing this, Toyota has adhered to the following principles:
Details are always transmitted from the previous stage to the next stage
When you don't receive a Kanban card, don't start production
Each box in the line needs to contain a Kanban card clearly stating: product details, place of production, destination, quantity.
Each box and each tray needs to contain the specified quantity, without excess
Do not hand over parts or waste products to the next stage
The time between deliveries and the number of Kanbans should be minimized
As a result, Kanban cards have indeed helped the team to strictly control each step in the production line. It's important that they all show alignment with previous workflows and carry sufficient information.
Later, engineer Taiichi Ohno and Toyota Corporation realized that the Kanban principle is not limited to the manufacturing sector, but can be applied to any other process or organization. That was the forerunner of the current Kanban management method.

1.3. Operating principle of Kanban
Today, the Kanban model is based on some basic principles as follows:
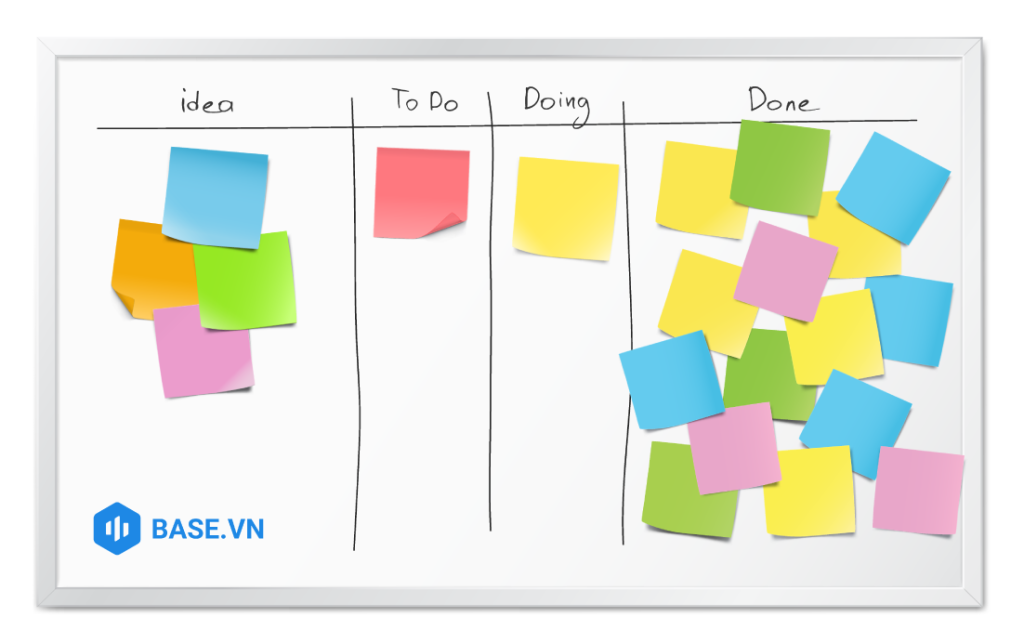
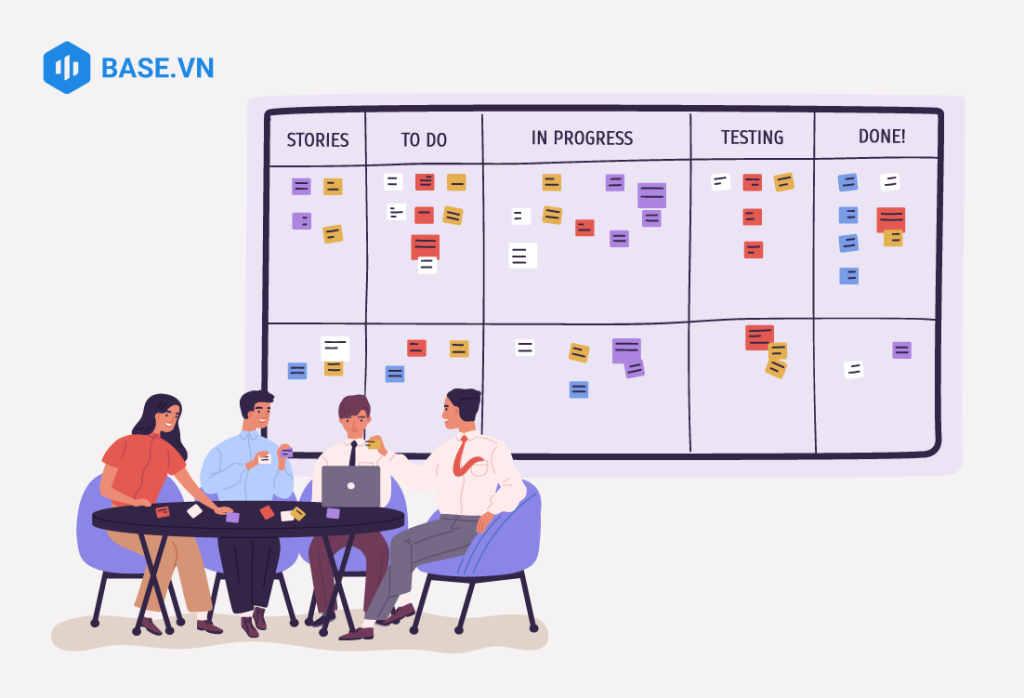
Workflow visualization: Kanban uses Kanban boards, columns, and cards to visualize tasks and workflows. Each card represents a task that needs to be done, and the columns on the board represent different stages of the workflow – also different states of the task. At its simplest, a Kanban board can include 3 columns: To-do, Doing, and Done.
Work In Progress Limit – WIP Limit : Kanban limits the amount of work done at once at each stage of the workflow. The amount of work for each person and each department also needs to be limited to a feasible level. This helps avoid overload and at the same time motivates people to increase focus on the current job instead of running multiple tasks at the same time.
Maintain workflow flow: The goal of Kanban is to optimize workflow, ensuring that work moves from one stage to the next coherently, without unnecessary delays. Moving the Kanban card to change the status of each task will be done sequentially according to the original regulations to avoid congestion.
Focus on continuous improvement : The production process is always improved continuously, even if it is already very good. Did you know that if you consistently make very small improvements to increase your productivity by 1% every week, after a year you can increase your productivity by up to 67%?
No products are defective.
2. Key concepts in the Kanban model
2.1. Job board
A task board (Kanban board) is a board containing the to-do items of a project or work process. In traditional management tools, this is called a "project" or "workspace". .
In a Kanban board, work cards are moved through columns that correspond to stages in the workflow, to represent the progress of the work. In addition, Kanban Boards can include additional information such as performance statistics, requests, notes, or other charts to assist in managing and tracking work progress.
Looking at the task board, the implementer can easily grasp the route to the plan's goal, the overall progress of the work flow, and outstanding information such as which tasks need to be prioritized. First, which jobs are about to expire and have expired,...
2.2. Job list column
A Kanban column is a concept used to describe sections of a Kanban board, each representing a different stage or state in the workflow. Work tags move through these columns as they are executed one after another through the workflow.
Each Kanban column will contain a List of cards - usually cards in the same stage of the process. In traditional project management, this is a “to-do list” or “task list.”
2.3. Job card
Work cards (Kanban cards) are used to visualize tasks in the workflow. Each task card represents a specific task, such as a task to be completed or a product to be realized. Kanban cards in traditional project management tools are called “to-dos” or “tasks”.
Each Kanban card will include necessary information such as:
Card title: Brief description of the task to be performed
Person in charge: Name of the person assigned to the task or responsible for that task
Estimated completion: A deadline or expected time to complete the task
Code: The number corresponding to each card, used to accurately identify and search for that card in the Kanban system
Color code or sticker: Marks the status of work cards, or identifies cards that have been classified
Priority marking: Signs to identify tasks that need to be prioritized for early implementation.
The job card is evidence of all activities that form work results. Therefore, every time the entire work process needs to be reevaluated, the management team can quickly check each job card to have a more detailed and accurate view.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of the Kanban method
Nothing is perfect, and the Kanban method has its advantages and disadvantages to keep in mind.
3.1. Advantage
Everyone is on the same plane: The Kanban method makes it easy for everyone to see all tasks and to-dos, bringing transparency to the entire work process. Accordingly, each member has the ability to eliminate unnecessary work and focus on the most important tasks.
Flexible work management: During the work process, new Kanban cards will be easily added, or their status and priority will be changed. Thanks to that, Kanban is considered a quick response model, helping the workflow easily respond to changing requirements.
Increase work productivity: The Kanban method requires people to focus on current tasks until they are completed, avoiding multitasking that causes process congestion or affects the output quality of work. This principle has helped tasks to be handled more neatly and scientifically, increasing actual work productivity.
Helps quickly detect bottlenecks in the process: When working on a Kanban board filled with job cards, it is not difficult to recognize bottlenecks in the process: some columns are overloaded with tasks, Some columns have been stuck for a long time, some cards have not been moved to another stage for a long time, etc. This is one of the outstanding advantages of the visualization method.
Simple system, easy to deploy: Thanks to the easy-to-understand usage principle and easy-to-set-up model, the Kanban method can be deployed in any team, business of any industry or scale. It can even be flexibly applied to different processes, or different stages of the project without causing too much disturbance.
3.2. Defect
Difficulty in estimating time: Kanban focuses on continuous work and does not place many time limits. The columns on the board correspond to work stages but do not have corresponding time frames, making it difficult to plan when tasks will be performed, and estimate when everything will be completed. .
Must update regularly: The Kanban method requires users to update the status of job cards regularly, even instantly; because otherwise, the team risks working with inaccurate information, and also loses the meaning of visualizing workflows into tables and columns.
Difficult to apply on a large scale: If in a work flow there are too many related activities or tasks that require frequent transitions, or there are tasks that do not meet the requirements and must change status. "Going back" to the previous stage, the Kanban board is easy to get confused. It will be difficult for the execution team to capture and keep up with all of this activity.
No guaranteed output: Kanban often focuses on transitioning statuses to cards in the workflow, so while it drives daily task execution, it can put the bigger picture at risk: small tasks are completed, but the final output – in the grand scheme of things – is not necessarily achieved.
3.3. So how is Kanban suitable for projects?
The Kanban method is most suitable in projects where priorities fluctuate to a high degree – even from day to day, especially projects that possess the following factors:
The project emphasizes a continuous workflow rather than single, critical deadlines
The project is facing a backlog due to work delays. The basic process is stable but operations need to be smoother and more efficient.
There is not much pressure on completion time
Need a flexible system to add, delete, and edit task information during work
Need continuous improvement in the working process
You want the team to have the ability to report results at any time
4. Compare Kanban, Scrum and Agile
4.1. Explanation of concepts
In essence, Agile is a methodology, an overarching philosophy based on iterative and incremental principles for project management. The goal of Agile is to help shorten product development time and bring products to customers as soon as possible.
Scrum is a framework that follows the Agile methodology, often used in product development projects where the end goal has not yet been determined by the user. Scrum focuses on optimizing value achieved in fixed time cycles lasting from 1-4 weeks, to continuously improve the product, technology, team and work environment.
On the other hand, Kanban is also a management model that belongs to the Agile family , which means it provides specific tools and processes for Agile implementation. It embodies many of the principles that characterize Agile methodology, including adaptability to change and promoting transparency across the entire team.
Therefore, essentially we will only need to compare Kanban and Scrum to clearly see the difference.
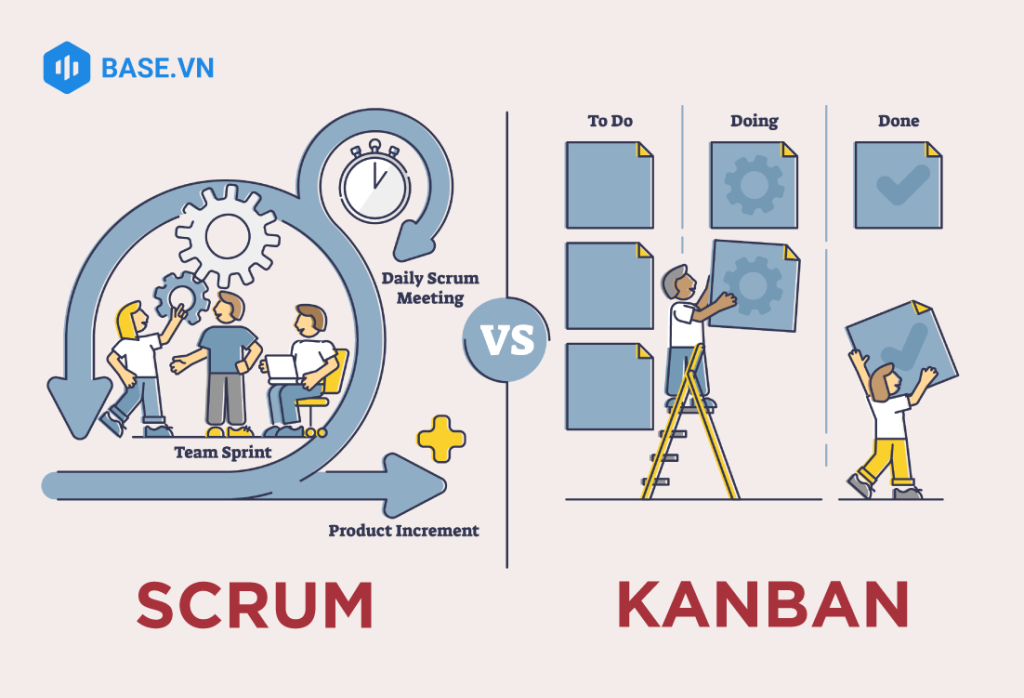
4.2. Compare Kanban and Scrum
Scrum
Kanban
Origin history
Software Development
Lean production
Principle operate
Continuously improve through implementing and evaluating the results of development iterations (Sprints)
Use visuals to visualize workflows and tasks (tables, columns, and cards)
Core principles
– Transparency – Adaptation – Inspection
– Effective – Efficient – Predictable
Workflow
There is a fixed duration, there is a sprint phase
Is a continuous flow
Implementation steps
– Build and manage Product Backlog – Sprint planning – Sprint execution – Daily meeting – Sprint review – Sprint improvement meeting
– Outline the workflow on the Kanban board – Set up WIP Limit for each column – Create Kanban cards – Start working – Improve the Kanban system
Team structure
Complete team with 3 specific roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Scrum Development Team
No specific roles are divided, can be applied to any team structure
Performance metrics
Completion speed Workload Team satisfaction
Cycle Time Total time from request to completion Efficiency of process flow
4.3. Should I choose Kanban or Scrum?
Depending on the scale and nature of the project, you can choose to apply the Kanban or Scrum model accordingly. Both of these approaches promise to make the implementation process more transparent, more efficient, and improved over time.
Or else, you can implement and manage projects in a model that combines (and is influenced by) both Kanban and Scrum – called Scrumban . Scrumban uses Scrum processes and Kanban visualization tools. For example, leveraged Kanban boards are a great tool for tracking individual tasks within a Scrum sprint.
5. Basic steps to implement Kanban
Step 1: Outline the workflow on the Kanban board
To implement Kanban, you need to start by having a whiteboard or online Kanban board. Then, separate your workflow into specific stages from start to finish. Draw columns on the board, each column representing one of the stages.
Step 2: Set WIP Limit for each column
To use the Kanban method effectively, you need to define and apply a concurrent workload limit (WIP Limit) to each Kanban column – the maximum number of jobs allowed to exist in that column at the same time. point. This step is to keep the workflow throughout the project smooth, avoiding work overload.
Considering your individual workload, you should also set a limit of only 2-3 tasks that need to be done at the same time. This number will help you concentrate better, not feel pressured by doing too many things at once, and also not reduce the quality of your work output.
Step 3: Create Kanban cards
Next, it's time to create the corresponding Kanban card for each job or task, and then place them on the corresponding column of the board. Each card should contain essential information such as title, person in charge, due date, and any additional information.
Note that you can arrange the cards in each column in order of priority – with the most urgent tasks at the top, so you have a clear view of the work in progress and know how to prioritize tasks reasonable.
You can also choose different colors for the cards to associate different types of work, urgency or priority (For example: Red is urgent, yellow is priority). second, blue is normal).
Step 4: Start working
Once you've deployed your Kanban board, you can start working on the work on the top card of each column. Once completed, move the card to the next column in the workflow. Note that you need to ensure compliance with WIP Limits to avoid overload and optimize performance.
If there are problems or obstacles during work, handle them quickly, to ensure the process is as smooth as possible.
Step 5: Improve the Kanban system
Don't forget to continuously collect feedback from your team and stakeholders (partners, customers, supporters) and use this information to improve the Kanban system – including the process work, structure of tables and columns, or how to arrange and label on Kanban cards,...
And after a regular period of time, you can count and summarize the status of the work cards: how many cards have moved to the last column, how many cards are overdue,... to Know the actual performance of individuals and teams. Through these numbers, it is possible to evaluate whether the Kanban method is really effective – compared to before using it, or before you made improvements to the system.
Read more: What is the Waterfall model? How to apply Waterfall to project management
6. Some management tools use the Kanban method
6.1. Trello task management application
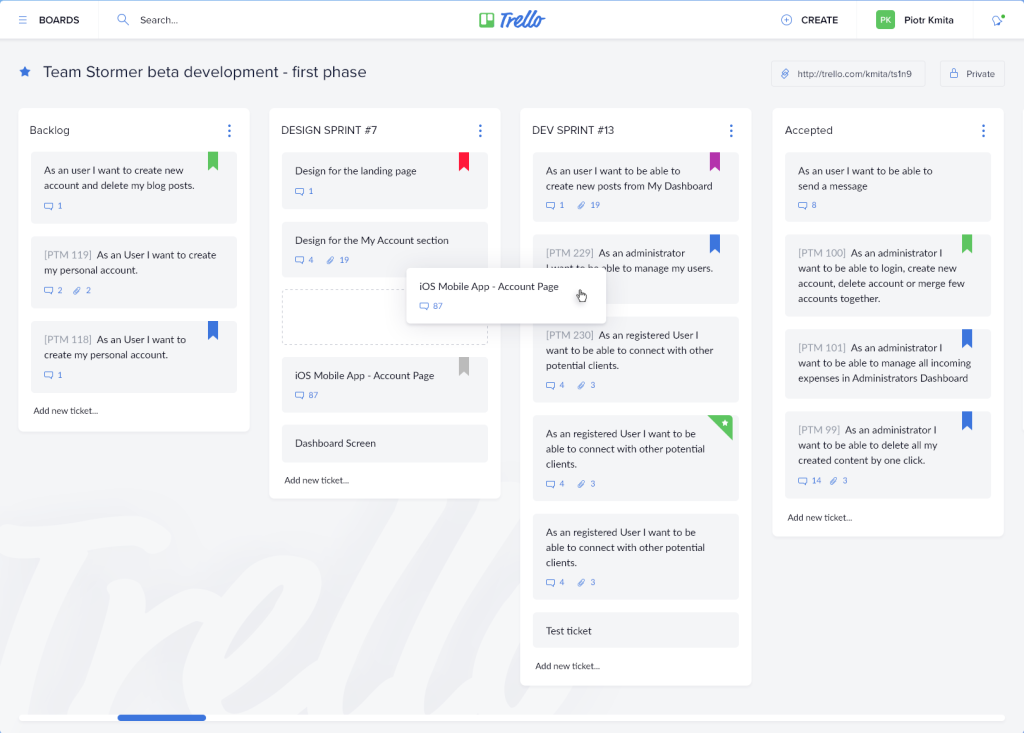
Trello is one of the popular work management tools based on the Kanban method. With a minimalist design, easy experience, plus a free version, Trello is popular for use by individuals or small teams.
Trello's working interface is identical to sticky notes stuck on a whiteboard. The columns are collectively called List, often applied to describe the steps of a simple process flow. For example: To-do > Step 1 > Step 2 > Step 3 > Complete.
On Trello, you can easily move Cards by drag-and-drop, from one List to another. The necessary information fields in each job card are guaranteed. In particular, group members can communicate directly with each other right in each Card, by leaving comments and tagging each other's names.
Trello's weaknesses are the hierarchy of admin members, no time management, and no reporting.
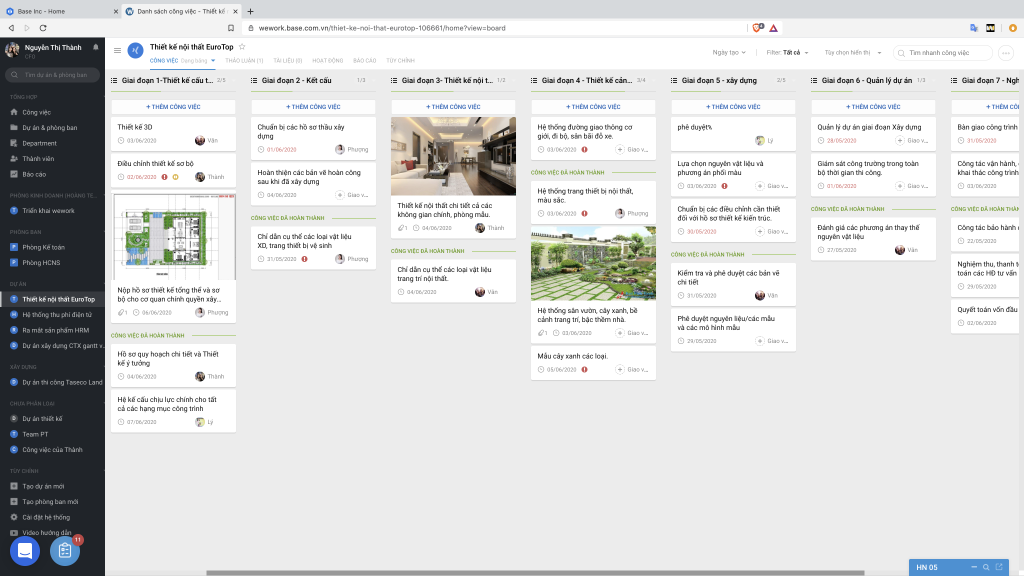
6.2. Base Wework project management software
In Vietnam, Base Wework is the leading project management software alternative to Trello.
Base Wework inherits Trello's optimized Kanban interface, but at the same time completely solves the disadvantages that Trello has :
Customize strict decentralization, transparency, support for an individual to participate in deploying and/or managing multiple departments and projects.
Intuitive and flexible progress tracking in a variety of methods, suitable for many purposes and project natures: not limited to the Kanban interface, data can also be flexibly converted to list formats ( to-do list), schedule format, Gantt chart format ,...
Built-in internal chat feature, allowing 1-1 online chat and group chat
Employees receive automatic reminders every day, including to-do lists and late alerts
Develop a feature to review work results, ensuring the work flow is not congested and ensuring output quality
In particular: There is a comprehensive reporting system on project implementation results, with data updated in real-time on the amount of work, implementation progress, and individual performance. core,…
With a set of professional and flexible features, Base Wework project management software is a tool favored by administrators, suitable for projects of all nature and scale.
6.3. Base Workflow business process management software
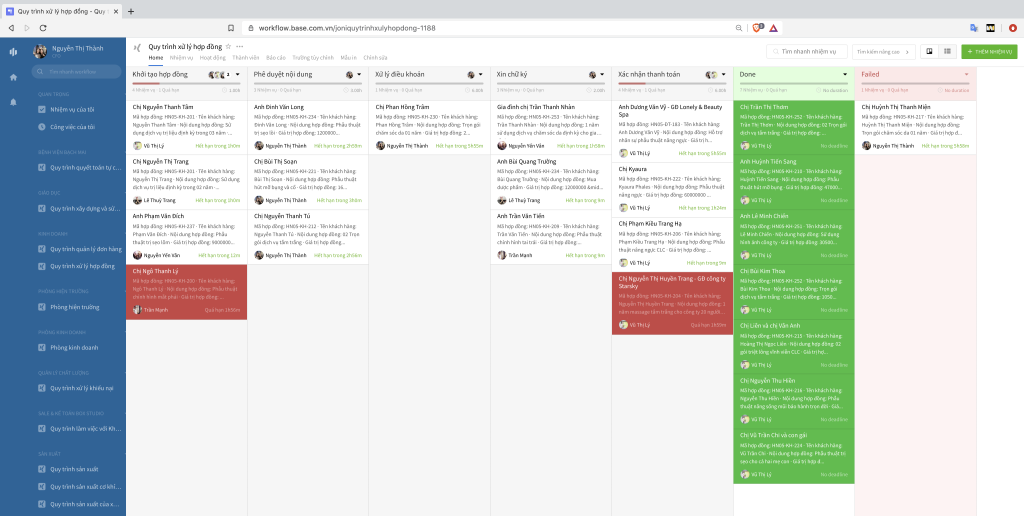
Also developed by Base.vn, Base Workflow is a 4.0 Business Process Management software , applying the Kanban method thoroughly and advancedly.
In each process, the software supports managing quantity, quality and progress accurately:
Set up an SLA (Service Level Agreement) which is a specific time limit for each step. The automatic timer has the ability to exclude holidays and non-working hours. When a task is overdue and has not been delivered, it will turn red for both employees and managers to recognize.
Inside each big task can be a list of small tasks. Only when they are all marked complete is the big task ready for handover. A handover is a task that will automatically include all attachments, information, results, notes, etc.
Each step in the process is responsible for one or more specific personnel. When the work is handed over to that step, the software will automatically assign the work and send a notification to the responsible person, on the principle of balancing the amount of work to be done between personnel.
There are detailed performance reports for each business process.
In particular, the power of Base Workflow is demonstrated in linking business processes into a comprehensive system, capable of automatically transferring between processes (For example: When a job is pulled - drop to the completion step of the Contract Processing Flow , it will be automatically forwarded to the Payment Flow ). This is a special feature that Trello and traditional Kanban tools do not have.
7. Conclusion
Managing work and processes is now easier with the Kanban method and supporting software. Kanban can be applied flexibly at many times - in many places - in many cases, as long as the implementer possesses system thinking and understands its principles.
Last updated