Elastic Search
Elasticsearchis a search engine based on the Apache Lucene. It provides a fully-tooled, distributed search engine with an HTTP web interface that supports JSON data. Elasticsearch is developed in Java and released as open source under the Apache license. (According to wikipedia)
If you wonder if you need to learn more Apache Luceneto understand clearly Elasticsearch, I would answer of course yes, but this research will take a lot of time and effort, so if you have time, you can learn more. If you don't have time, you just need to simply understand Apache Lucene it as core of Elasticsearchas phpcore of laravel. You just need to understand Elasticsearchbecause we just work with you Elasticsearchand if Apache Luceneyou understand then it's a plus point, otherwise, it's okay.
In short :
ElasticsearchIs onesearch engine.Elasticsearchinherited fromLucene ApacheElasticsearchessentially acts as a web server, capable of searching quickly (near real-time) through the RESTful protocolElasticsearchAble to analyze and compile dataElasticsearchruns on a separate server and at the same time communicates via RESTful so it does not depend on what the client is written in or what your current system is written in. So integrating it into your system is easy, you just need to send an http request and it returns results.Elasticsearchis a distributed system with excellent scalability. Add more nodes to it and it will automatically expand for you.Elasticsearchis 1open sourcedeveloped byJava
User :
Wikimedia Commons
athenahealth
Adobe Systems
Facebook
StumbleUpon Mozilla,
Amadeus IT Group
Quora
Foursquare
Etsy
SoundCloud
GitHub
FDA
CERN
Stack Exchange
Center for Open Science
Reverb
Netflix
Pixabay
Disturbed
Sophos
Slurm Workload Manager
Concepts you need to know
1, Document
The document is a JSON object with some data. This is the basic information unit in ES. In a basic way, this is the smallest unit to store data in Elasticsearch.
It is the basic unit of data in Elasticsearch- a JSON object with some specific data. Each document belongs to a type and is in an index. Each document is associated with a unique identifier called a UID.
ElasticsearchUse inverted index to index documents. An inverted index is a unit-based indexing method that creates links between words and documents containing those words.
2, Index.
IndexPerhaps it is a very familiar concept for those of you who have used Mysqlit. By reading this, you probably already understand what its function indexis. However, if you think that indexin is ESexactly the same as in Mysql, then you are wrong!
In Elasticsearch, use a structure called inverted index. It is designed to allow searching full-text search. Its method is quite simple, the documents are separated into each meaningful word and then mapped to see which text belongs to it. When searching, depending on the type of search, specific results will be given.
For example: We have 2 specific documents as follows:
To create a inverted index, we will first split the content of each document into separate words (which we call terms), create a sorted list of all termsuniques, and then list which documents where each term appears. The following results:
Now, if we want to search for color quick brown, we just need to look in the documents in which each term appears or not. The following results:
As you can see, both pieces of text are suitable for the keyword. However, it can be easily seen that Doc_1 is much more accurate. You can absolutely set up the search more carefully, but I will mention this issue in the next article. If you are interested, you can go to the documents https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/guide/current/inverted-index.html and https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/ elasticsearch/guide/current/relevance-intro.html#relevance-intro for a clearer view.
3, Shard
Shardis the object ofLucene, which is a subsetdocumentsof 1 Index. An Index can be divided into many shards.Each
nodeincludes multipleShard. That's whyShardit is the smallest object, operating at the lowest level, playing the role of data storage.We almost never work directly with customers
ShardbecauseElasticsearchwe support all communication and automatically make changes whenShardnecessary.There are 2 types
Shard:primary shardandreplica shard.
3.1 : Primary Shard
Primary Shardwill store the data and typeindex. After typing, the data will be transported to theReplica Shard.The default of
Elasticsearcheachindexwill be 5Primary shardand eachPrimary shardwill come with 1Replica Shard.
3.2 : Replica Shard
Replica ShardAs its name suggests, it is a place to store cloned dataPrimary ShardReplica Shardplays a role in ensuring data integrity whenPrimary Shardproblems occur.In addition,
Replica Shardit can help increase search speed because we can set the number toReplica Shardbe more than the default ofES
To understand more about Primary Shardhay, Replica Shardpeople can go here to learn more. In this article, Mr. Long wrote in quite detail about the concepts as well as how storage and retrieval work, ESso I would like to not say anything more about this part.
4, Node
Is the operational center of Elasticsearch. It is a place to store data, participate in performing typing
indexasclusterwell as performing search operationsEach
nodeis identified by a unique name
5, Cluster
Group activities
nodestogether, sharing the same propertiescluster.name. Therefore,Clusterit will be identified by a 'unique name'. Identifying names withclusterthe same name will cause errors for the nodes, so when setting up you need to pay close attention to this pointEach cluster has a
nodemaster, which is automatically selected and can be replaced if a problem occurs. A cluster can consist of 1 or morenodes. Nodes can operate on the same server. However, in reality, oneclusterwill include manynodesoperations on different servers to ensure that if one server has a problem, the other server (another node) can operate fully functionally compared to when there are 2 servers. Theynodecan find each other to operate on the same cluster through the protocolunicast.
Its main function Clusteris to decide what shardsgets allocated to nodewhat and when to move the numbers Clusterto rebalanceCluster
Advantages and disadvantages of ES
Advantage
Very fast, powerful data search based on Apache Lucene (near-realtime searching)
Ability to analyze data (Analysis data)
Excellent horizontal “tap” scalability
Fuzzy search support, meaning that even if the search keyword has misspellings or incorrect syntax, it is still possible for elasticsearch to return good results.
Supports Structured Query DSL (Domain-Specific Language), providing specific and clear specification of complex queries using JSON. You can learn more here
Supports many
Elasticsearcclients such asJava,PhP,Javascript,Ruby,.NET,Python
Defect
Elasticsearchdesigned for search purposes, so for tasks other than search such as CRUD, Elastic is inferior to other databases such as MongoDB, and Mysql... Therefore, people rarely use Elasticsearch as the main database but often combine it with another database.There
elasticsearchis no conceptdatabase transaction, meaning it will not ensure data integrity in operationsInsert,Update,Delete. That is, when we make changes to many records if an error occurs, it will make our logic wrong or not. leading to data loss. This is also part of the reason whyelasticsearchit should not be the main database.Not suitable for systems that regularly update data. It will be very expensive to index data.
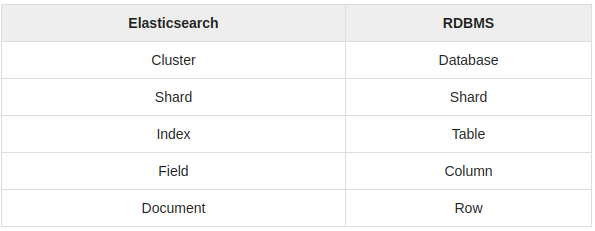
Elasticsearch vs RDBMS
Last updated